Research and Application of Key Technologies for Ultra - deep Composite Directional Drilling in the Yangtze River to Hanjiang River Water Diversion and Hydropower Project
(1) Project Situation:
The water conveyance tunnel of the Water Diversion from the Yangtze River to the Han River Project features a large burial depth and a long tunnel alignment. The topographical and geological conditions and the geological structural background along the line are complex, and the karst hydrogeological conditions are also intricate. There exist engineering geological problems and environmental geological problems such as water inrush and mud burst, high external water pressure, hard rock, rock burst, soft rock deformation, drainage of surface water and groundwater, harmful gases and radioactivity, and high ground temperature. The tunnel construction will face the risks brought about by these problems. The tunnel passes through a fault zone and overlaps with the soluble rock cave section, so the risks of water hazards such as sudden water inrush will be even higher (see Figure 10-4 for the project site situation). Due to the special topography and geological conditions and the great difficulty of coring in the track-changing section, the borehole wall collapsed during the construction process, which brought great difficulties to the subsequent construction. In order to meet the requirements of coring and directional drilling in the track-changing section, grouting management was carried out for the collapsed well section. Through grouting reinforcement, the measured trajectory of Branch 3 conforms to the expected designed trajectory, and the coring rate meets the requirements (Figure 10-4, Figure 10-5).

The on-site construction situation of the project
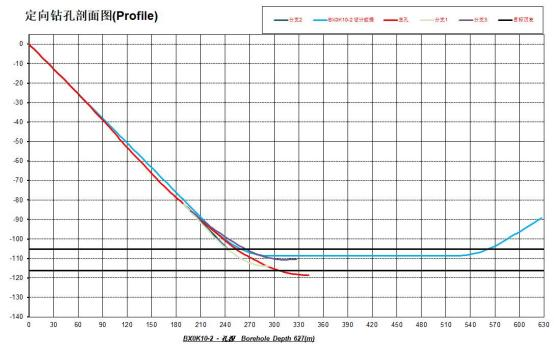
Sectional Diagram of the Directional Borehole
(2) Material Usage Situation:
By using MidwestSGS - type materials for grouting and plugging leaks.





